Mastering Conditional Statements in Python : The 5 Powerful Tools
Introduction:-
Conditional in python allows us to run code only when a specific condition is true. They help us make decisions and control how our program flow based on comparison, values or logical conditions.
For example,
age = 20
if age >= 18:
print(“You are eligible to vote.”)
Output :-
You are eligible to vote.
In this example we used an if statement to check if the age is 18 or more and printed a message based on the condition.
What are Conditional Statements in Python?
A conditional statement in python determines the flow of code execution and it’s direction based on certain conditions. It decides the control flow of a python program according to the output of the given condition.
Conditional in python enable conditional execution of a statement or a group of statements based on the expression’s value. For example, we can segregate even and odd numbers using if- else statements in python.
Types of Conditional Statements in Python
We can use different combinations of conditional statements in python to implement our code during decision making scenarios. Below we have explained different types of conditional statements in python.
1. Python if Conditional Statement
2. Python if-else Conditional Statement
3. Python Nested if Conditional Statement
4. Python if-elif-else Conditional Statement
5. Python Ternary Expression
1. Python if Conditional Statement
The if statement in python is the simplest decision-making statement to execute a block of code. It tests the given condition, and if the condition is true, it execute the if block of code. The specified condition can be a valid logic expression needed to be evaluated as True or False.
Python considers all non-zero values True, whereas None and 0 are False. We can also write a single if statement without adding an else block. However we can’t write an else statement without an if statement in python.
Syntax of the if Statement
if condition:
# Statements to execute if
# condition is true
Here the code evaluates the expression. If the given condition is fulfilled, the code will be executed; otherwise, it will not. If the evaluated condition is False, it will not execute the block of code. We use the condition through parentheses ().
Flowchart of the if Statement
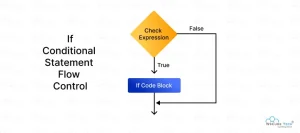
Example :-
x = 10
if x > 5:
print(“x is greater than 5”)
Output-
x is greater than 5
2. Python if-else Conditional Statement
The python if statement executes a block of code only when the given condition is true; if it is false, it doesn’t execute anything. So, the if – else statement addresses this issue by merging the else statement, which is executed when the condition is false.
So, if condition is true, the program executes the if block of code; if the condition is false, it executes the if else code block.
Syntax of the if-else Statement
if (condition):
# Executes the statement 1 if
# condition is true
Else:
# Executes the statement 2 if
# condition is false
Flowchart of the if-else Statement
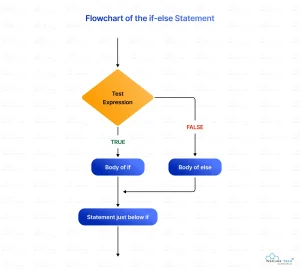
Example
x = 3
if x > 5:
print(“x is greater than 5”)
else:
print(“x is not greater than 5”)
Output-
x is not greater than 5
3. Python Nested if Conditional Statement
The nested if conditional statement in python places an if statement inside another if statement. We use it to test and evaluate multiple possibilities and filter a variable several times. The nested if statement requires us to focus on correct indentation to define the scope of each statement, especially when there are multiple blocks of nested if statement.
We can include as many nested if statements as we want, but it can make the code less optimized hampering it’s readability. Therefore, minimize the use of Python nested if statements.
Syntax of Nested If Statement
if (condition1):
# Executes if condition 1 is true
if (condition2):
# Executes if condition 2 is true
# if Block (condition 1) ends here
# if Block (condition 2) ends here.
Flowchart of Nested If Statement

Example
a = 7
b = 10
c = 7
if a + b > c and a + c > b and b + c > a:
print(“The sides form a valid triangle.”)
if a == b == c:
print(“The triangle is Equilateral.”)
elif a == b or b == c or a == c:
print(“The triangle is Isosceles.”)
else:
print(“The triangle is Scalene.”)
else:
print(“The sides do not form a valid triangle.”)
Output-
The sides form a valid triangle.
The triangle is Isosceles.
4. Python if-elif-else Conditional Statement
Python executes the if statement from top to bottom. So, if one condition is fulfilled and is evaluated to be true, the program executes the statement associated with it and skips the remaining statement. If no condition is true, it executes the else statement. Basically the if-else statement executes a block of code between two alternatives. However, what if we have to choose between more than two alternatives ? That is where we use the if-elif-else statement in python.
The elif statement follows the if-else-if ladder statement and allows us to check multiple conditions in python , executing a code block based on true condition among them. We can add several elif statement in the code. It tests all the statement in the order and if all of them are false, it checks the elif statements. If the condition is true it executes the block after the if statement and skips the rest of statements. If no condition is true, it executes the else statement.
Syntax of if-elif-else Statement
if expression1:
print(statement_if)
elif (expression2):
print(statement_elif)
else:
print(statement_else)
if condition1:
# code block 1
elif condition2:
# code block 2
else:
# code block 3
Flowchart of elif Statement

Example
score = 70
if score >= 90:
print(“Grade: A”)
elif score >= 60:
print(“Grade: B”)
else:
print(“Grade: C”)
Output:-
Grade: B
5. Python Ternary Expression
The ternary expression allows us to write a python conditional statement in one line. It helps decide what value to return based on a condition, making the code shorter and cleaner.
Shorthand if in Python:-
We use this when we want to return a value if a condition is true and do nothing otherwise.
Syntax:-
if expression: statement
Example:-
score = 78
if score >= 33:print(“Pass”)
Output-
Pass
Shorthand if-else in Python
We use the if-else ternary expression to choose between two values depending on whether the condition is true or false.
Syntax:-
value_if_true if condition else value_if_false
Example:-
marks = 75
result = “Pass” if marks >= 40 else “Fail”
print(result)
Output:-
Pass
Frequently asked question:-
Q 1. Why are conditional statements called the decision-making statements in Python ?
Ans:- Conditional statements are called decision-making statements because they allow your program to make choices and perform different actions based on specific conditions. Instead of running all code in a straight line, they help your program decide what to do next, making your code smarter and more flexible.
Q 2. Can i use conditional statements inside loops in python ?
Ans:- Yes ! You can use conditional statements inside loops to make your code more powerful and flexible.
You can also check the official Python documentation on conditional statement to learn more in detail.
Check our homepage for more tutorials and guides.
