CSS Full Course – In this complete guide, you will learn how to use CSS to style websites with confidence.
Introduction to CSS
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets. It is the language used to style and design web pages. While HTML is used to create the structure of a webpage, CSS is used to control how that structure looks — including layout, colors, fonts, spacing, and more.
With CSS, you can make your website visually appealing and user-friendly by applying styles to individual elements or entire sections.
**CSS Full Course – 2025 Beginner**: Welcome to the most comprehensive and beginner-friendly CSS full course. In this guide, you’ll learn how to style websites using modern CSS properties, selectors, layouts, and best practices. Whether you’re starting from zero or brushing up your skills, this CSS Full Course has everything you need to become confident in web styling.
Learn CSS Basics in This CSS Full Course
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is the language used to style and design web pages. In this CSS full course, you’ll begin by learning how to apply colors, set layouts, and control fonts using simple CSS properties. This section is perfect for beginners who want to build a strong foundation in web design.
What is CSS?
CSS is the language we use to style a Web page.
- CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets
- CSS describes how HTML elements are to be displayed on screen, paper, or in other media
- CSS saves a lot of work. It can control the layout of multiple web pages all at once
- External stylesheets are stored in CSS files

Why Use CSS?
CSS is used to define styles for your web pages, including the design, layout and variations in display for different devices and screen sizes. This CSS full course will guide you step by step.
For Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
background-color: white;
}
h1 {
color: black;
text-align: center;
}
p {
font-family: verdana;
font-size: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My First CSS Example</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Output
My First CSS Example
This is a paragraph.
CSS Syntax
This section introduces you to basic CSS concepts such as syntax, selectors, colors, and how to connect your CSS with HTML. As part of this CSS Full Course, you’ll get practical tips and examples to learn faster.
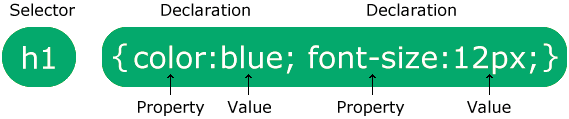
The selector points to the HTML element you want to style.
The declaration block contains one or more declarations separated by semicolons.
Each declaration includes a CSS property name and a value, separated by a colon.
Multiple CSS declarations are separated with semicolons, and declaration blocks are surrounded by curly braces. This CSS full course will guide you step by step
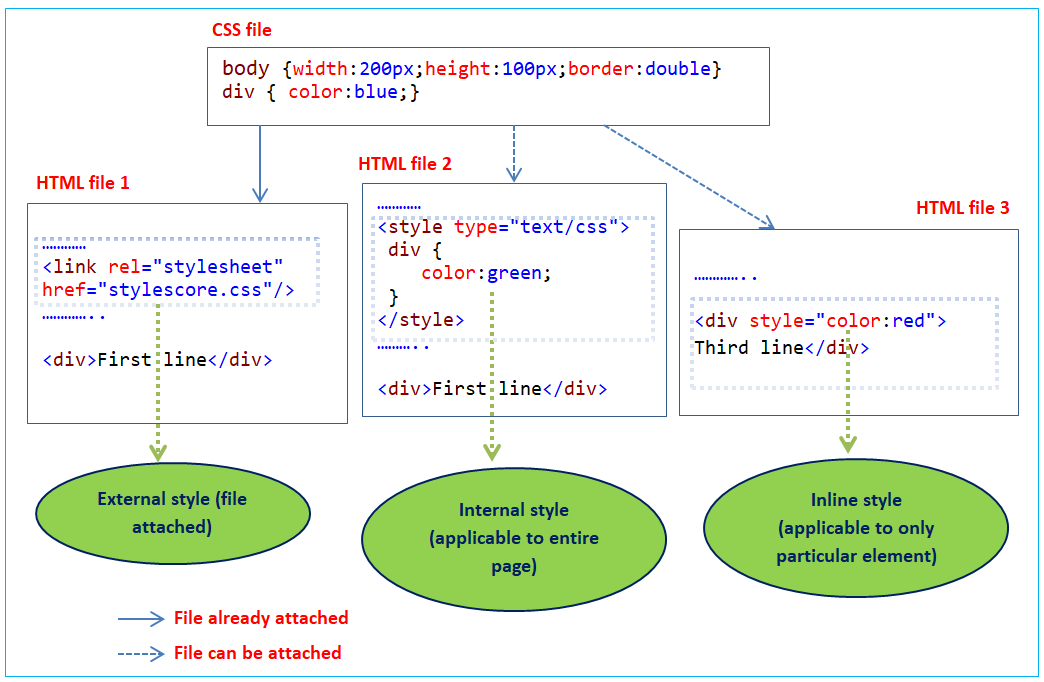
Type of CSS
There are three main of CSS. This CSS full course will guide you step by step of type of CSS
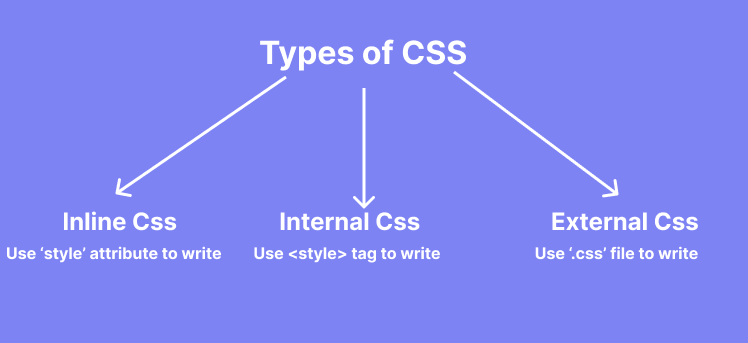
1. Inline CSS
-
CSS is written directly inside the HTML element using the
styleattribute. -
It applies to only that specific element.
🔹 Example:
2. Internal CSS
-
CSS is written inside a
<style>tag within the<head>section of the HTML document. -
It applies to the entire HTML page.
🔹 Example:
3. External CSS
-
CSS is written in a separate file with a
.cssextension. -
That file is linked to the HTML document using the
<link>tag. -
It can be used for multiple HTML pages, making it ideal for large websites.