“In this guide, we will explore Distributed Version Control in Git and understand how it helps developers collaborate seamlessly on projects.”
Git distributed version control** is a powerful system that allows developers to work collaboratively…
Git has become the backbone of modern software development. As a distributed version control system, Git allows developers to collaborate seamlessly…
Introduction
“In this guide, we will explore Distributed Version Control in Git and understand how it helps developers collaborate seamlessly on projects.”
Git has become the backbone of modern software development. As a distributed version control system (DVCS), Git allows developers to collaborate seamlessly, maintain a complete history of their projects, and work offline without relying on a central server.
In this Part 4 of our Git series, we will explore advanced Git concepts, workflows, and collaboration strategies that are crucial for managing complex projects. Whether you are a beginner aiming to understand distributed version control or a professional looking to optimize team collaboration, this guide provides practical examples, best practices, and step-by-step instructions to help you master Git in a distributed environment.
**Git distributed version control** has revolutionized how teams collaborate on software projects. With **Git distributed version control**, every developer has a complete copy of the repository, enabling offline work, fast commits, and seamless collaboration across locations. Learning **Git distributed version control** helps developers track changes efficiently and reduce conflicts in complex projects.
By the end of this guide, you will be able to:
-
Understand the core principles of distributed version control.
-
Use branches, commits, and pull requests effectively.
-
Collaborate with teams efficiently using Git workflows.
-
Avoid common pitfalls and resolve conflicts like a pro.
Git has revolutionized the way developers manage code. As a distributed version control system, it allows teams to work collaboratively across multiple locations while keeping the project history intact. In this Part 4 of our Git series, we will explore advanced Git concepts, distributed workflows, and collaboration strategies to help you become a Git expert.
Whether you are a beginner wanting to understand Git workflows or a professional looking to improve your collaboration skills, this guide covers everything you need to master Git in a distributed environment.
Git has completely changed the way developers manage and collaborate on code. As a distributed version control system (DVCS), Git allows multiple developers to work on the same project simultaneously, keep track of every change, and maintain a complete project history.
In Part 4 of this series, we will dive deep into advanced Git concepts, distributed workflows, branching strategies, and real-world collaboration techniques. Whether you are a beginner or a professional, this guide will help you master Git in a distributed environment.
Mastering Git: Distributed Version Control System – Part 4
Git is a powerful distributed version control system used by developers worldwide. In this fourth part of our series, we will dive deeper into advanced Git concepts, workflows, and collaboration techniques to help you manage projects efficiently.
Git Distributed Version Control Basics
### Benefits of Git Distributed Version Control
What is Distributed Git Workflow?
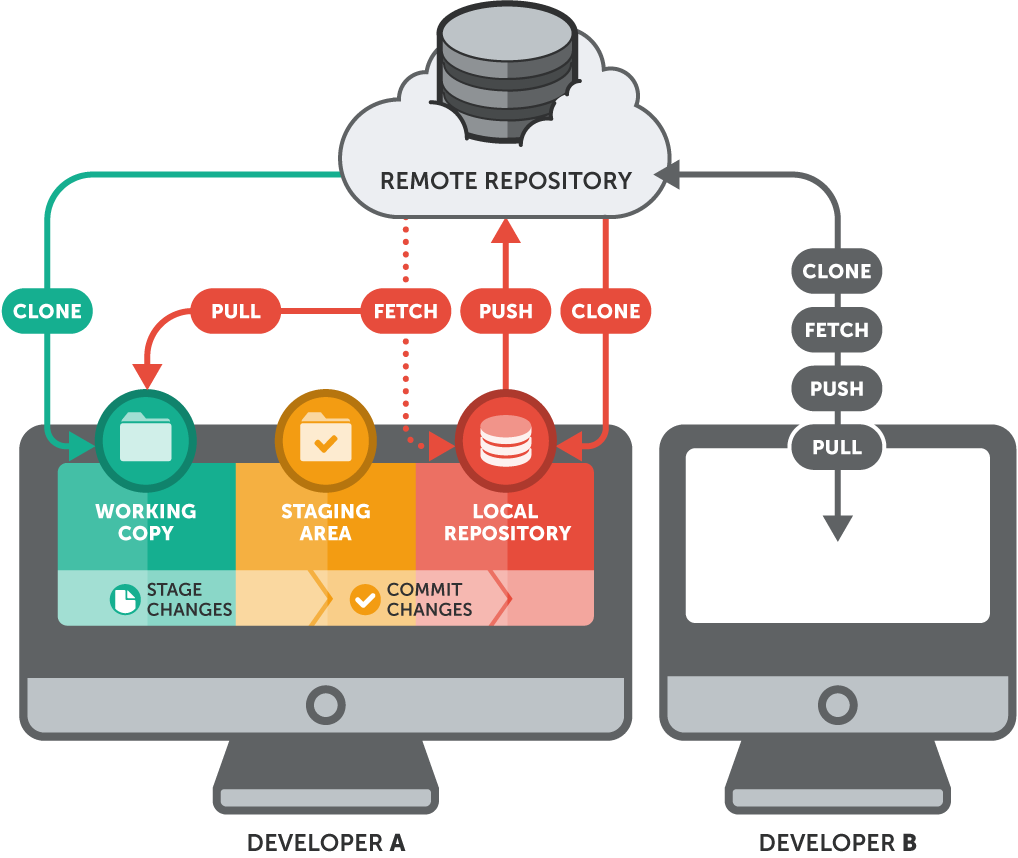
A distributed version control system (DVCS) means every developer has a complete copy of the repository, including its full history. Unlike centralized systems, Git allows you to work offline, commit locally, and push changes when ready.
## What is Distributed Version Control in Git?
Benefits of Distributed Version Control:
-
Work offline with full repository history
-
Faster operations due to local commits
-
Easy branching and merging
-
Collaboration without central server dependency
Git Workflow for Distributed Version Control
Git provides flexible workflows to manage code collaboratively:
1. Feature Branch Workflow
-
Create a branch for each new feature
-
Develop and test locally
-
Merge into the main branch when complete
2. Git Forking Workflow
-
Fork a repository to your own account
-
Make changes in the fork
-
Submit a pull request to the main repository
3. Git Pull Request Workflow
-
Collaborate through pull requests
-
Review code before merging
-
Maintain a stable main branch
Key Git Commands in Distributed Systems
Here are essential Git commands to master distributed version control:
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
git clone |
Copy a repository to your local machine |
git fetch |
Retrieve changes from remote without merging |
git pull |
Fetch and merge changes from remote |
git push |
Upload local commits to remote |
git branch |
List or create branches |
git merge |
Combine changes from different branches |
git rebase |
Integrate changes from one branch to another |
-
“In this guide, we will explain Git Distributed Version Control in detail.”
-
“The power of Git Distributed Version Control lies in collaboration and efficiency.”
-
“Developers prefer Git Distributed Version Control because it is reliable and fast.”
Best Practices for Git Collaboration
-
Commit Often: Smaller, frequent commits make collaboration easier.
-
Write Clear Commit Messages: Describe what and why you changed.
-
Use Branching Strategically: Keep your main branch stable.
-
Regularly Pull Changes: Stay updated with teammates’ work.
-
Resolve Conflicts Carefully: Review conflicts before merging.
-
How Git distributed version control solves conflicts
Common Git Distributed Issues & Solutions
-
Conflict During Merge: Use
git statusandgit merge --abortif needed. -
Out-of-Sync Repositories: Regularly
git fetchandgit pull. -
Accidental Commit in Wrong Branch: Use
git cherry-pickorgit reset.
Conclusion
Distributed version control in Git empowers developers to collaborate efficiently, work offline, and manage complex projects. Mastering these workflows and commands ensures smoother development and fewer conflicts.
Stay tuned for Part 5, where we will explore Git Hooks and Automation for advanced project management.
**Git distributed version control** allows developers to work offline and collaborate efficiently.
Teams using **Git distributed version control** can manage branches, pull requests, and merges without conflicts.
By mastering **Git distributed version control**, you can improve workflow and team productivity.
Want to learn about debugging techniques Click here