Introduction
In today’s world, artificial intelligence (AI) powers everything from voice assistants to self-driving cars. At the core of this revolution lies the Neural Network, a computational model inspired by the human brain. Neural networks allow machines to recognize patterns, make predictions, and learn from data in ways that were once thought to be uniquely human.
Neural Network
Neural network, or artificial neural networks, are a crucial aspect of machine learning that straight connects it to the broader field of AI. These networks are essentially computational systems, consisting of code written in programming languages—either high-level or low-level—and can be embedded in hardware such as chip systems. Neural networks can be executed as an Apps, allowing application engineers to utilize their capabilities without needing to delve into the intricate technical details of how they work.
Neural networks derive their name from biological neural networks, a concept first developed around the 1940s. The original idea, though no longer a leading theory in biology, suggested that the brain functions by activating a sequence of neurons, or nerve cells. These neurons take in stimuli—such as what we see, hear, or experience—and when certain thresholds are met, they “fire,” sending electrical impulses through a chain of neurons. This sequence ultimately leads to an output.
For example, if you touch a hot plate, the temperature triggers a chain of neural activations that quickly sends a signal to your muscles to pull your hand away, reducing exposure to harm.
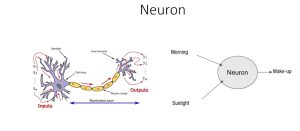
This process of continuous neural activation—connecting input stimuli to output actions—was the inspiration for artificial neural networks. These biological processes were converted in computer programs to create artificial versions of neural networks.
At its core, a neural network operates like a “black box” that takes in input (e.g., detecting day or night) and, based on that input, produces an output (e.g., deciding to wake up or stay asleep). While modern neuroscience shows that the brain is far more complex than this simplified model, the basic idea is robust enough to build artificial systems that mimic certain aspects of human intelligence, leading to the advancements we see today.
The process of how this activation occurs will be discussed in the next blog.
How Neural Networks Work
Imagine you want a neural network to recognize if a photo contains a cat. Here’s the process:
-
Input: The photo is broken down into pixel values (numbers).
-
Hidden Layers: The network detects features such as edges, shapes, and textures.
-
Activation Functions: Non-linear functions (like ReLU or Sigmoid) help the network learn complex patterns.
-
Output: The final layer gives a probability score (e.g., 95% cat, 5% not cat).
This ability to automatically extract and learn features makes neural networks extremely powerful.
Types of Neural Networks
There are different types of neural networks, each suited for specific tasks:
-
Feedforward Neural Network (FNN): The simplest type, where data flows in one direction from input to output.
-
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN): Specially designed for image and video recognition by detecting patterns in pixels.
-
Recurrent Neural Network (RNN): Best for sequential data like text, speech, or time series because they remember past inputs.
-
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): Two networks competing against each other to generate realistic data (used in deepfake technology).
-
Transformer Models: Advanced architectures powering large language models like GPT, enabling state-of-the-art performance in natural language processing.
Applications of Neural Networks
Neural networks are everywhere today. Some key applications include:
-
Healthcare: Detecting diseases from medical images, predicting patient outcomes.
-
Finance: Fraud detection, stock market prediction, and algorithmic trading.
-
Transportation: Autonomous vehicles using CNNs to detect pedestrians, traffic lights, and obstacles.
-
Entertainment: Recommendation engines on Netflix, Spotify, and YouTube.
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Chatbots, translation, sentiment analysis, and large language models.
-
Cybersecurity: Identifying unusual patterns to prevent data breaches.
Benefits of Neural Networks
-
High Accuracy: Neural networks can outperform humans in certain tasks (e.g., image recognition).
-
Automation: Reduces manual work by automatically learning features.
-
Adaptability: Can handle complex, non-linear relationships in data.
-
Scalability: Works efficiently with large datasets, making it ideal for big data.
Challenges of Neural Networks
Despite their advantages, neural networks are not perfect:
-
Data Hungry: Require massive amounts of labeled data to perform well.
-
Computational Cost: Training deep networks needs high-performance GPUs.
-
Black Box Problem: Hard to interpret how decisions are made.
-
Overfitting: Networks can memorize training data instead of generalizing.
-
Ethical Concerns: Used in areas like surveillance or deepfakes, raising privacy issues.
The Future of Neural Networks
The future looks promising as researchers are developing more efficient and explainable networks. With innovations like quantum computing, neuromorphic chips, and self-supervised learning, neural networks will become even more powerful and accessible.
They are expected to play a major role in fields such as personalized medicine, climate modeling, space exploration, and advanced robotics.
Conclusion
Neural networks are the backbone of modern AI, enabling machines to learn, adapt, and perform complex tasks. From healthcare to finance, they are transforming industries and shaping our daily lives. While challenges like data requirements and explainability remain, the opportunities are incredible.
As technology evolves, neural networks will continue to push the boundaries of what machines can do — bringing us closer to a future where AI is an integral part of every aspect of human life.
Check out more Blogs – Click here
Visit LinkedIn page – Click Here
