SDLC & DevOps-Introduction
SDLC – Software Development Life Cycle (In Detail)
SDLC is a structured process that helps software developers build high-quality software in a systematic way. It involves different steps and methods to develop and maintain software efficiently.

Phases of SDLC (With Explanation)

Requirement Phase
-
This is the first and most important step after planning.
-
In this phase, the development team meets the client to understand what kind of software they want.
-
Every small detail like features, design ideas, user needs, etc., are discussed and written down.
-
The main goal is to gather full and clear requirements so nothing is missed later.
Design Phase
-
In this phase, a blueprint (design plan) of the software is created.
-
It includes system architecture, data models, user interface designs, and how each part of the system will work.
-
Developers and designers work together to make sure the software design matches the client’s expectations.
Development Phase
-
After the design is ready, the actual coding begins in this phase.
-
Developers select the right programming languages, tools, and frameworks to build the software.
-
The application is developed module by module (step-by-step).
-
This is the core part where the software starts taking shape.
Testing Phase
-
After development, the software is tested to check:
-
If it is working correctly
-
If there are any bugs or errors
-
If it meets the client’s requirements
-
-
Different types of testing are done like unit testing, integration testing, system testing, user testing etc.
-
The goal is to fix issues before the software is released.
Implementation Phase
-
Once the testing is successful, the software is deployed (launched) to the live environment.
-
Real users start using the software.
-
This phase is also called the deployment phase, and it includes final setup and configurations.
Maintenance Phase
-
This is the long-term support phase.
-
After users start using the software, they might face some problems or need changes.
-
Developers continuously monitor the system and provide updates, fixes, and improvements.
-
This phase ensures the software remains useful and up-to-date.
SDLC & DevOps-Introduction (In Detail)
Different methodologies are used to follow SDLC based on project needs. Here are the three most common:
Waterfall Methodology

-
One of the oldest and simplest models.
-
Each step is completed one after another (like water flowing down steps).
-
You can’t go back to the previous step once it’s completed.
Advantages:
-
Easy to manage for small projects.
-
Everything is well-documented and planned in advance.
-
Deadlines and goals are clearly defined.
Disadvantages:
-
Not flexible – changes are hard to manage.
-
Not ideal for big or long-term projects.
-
Difficult to fix mistakes found later.
-
Can delay feedback as clients see the product only at the end.
Agile Methodology

-
Agile is an iterative and flexible method.
-
The project is broken into small parts called iterations or sprints (1–3 weeks).
-
After each sprint, a working version of the software is shown to the client for feedback.
Advantages:
-
Promotes team collaboration and fast feedback.
-
Great for projects where requirements change frequently.
-
New features are delivered quickly.
-
Encourages learning and improvement after each sprint.
Disadvantages:
-
Needs strong project leadership and good planning.
-
Too much dependence on customer communication.
-
Less documentation makes it hard for new team members to understand the project quickly.
-
If customer is confused or unclear, project may go in the wrong direction.
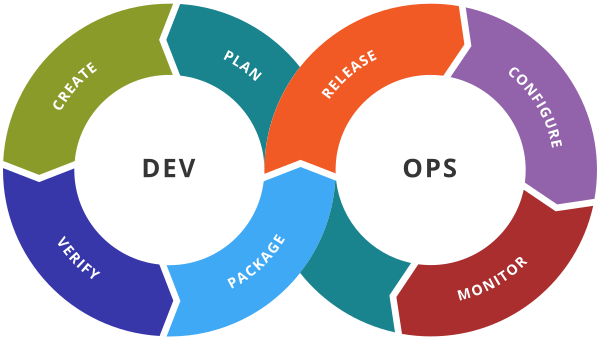
DevOps Methodology

-
DevOps stands for Development + Operations.
-
It focuses on team collaboration, automation, and continuous delivery.
-
DevOps helps to build, test, and release software faster and more reliably.
Key Features:
-
Developers and IT operations team work together.
-
Automation tools are used for testing, integration, and deployment.
-
Software is delivered in small, frequent updates.
-
Focus on monitoring and improving software continuously.
Benefits:
-
Faster delivery of software
-
Fewer errors during deployment
-
Better team communication and quick response to issues
Conclusion:
Each SDLC methodology has its own strengths.
-
Use Waterfall for simple, short-term projects with clear requirements.
-
Use Agile for projects with changing needs and close client involvement.
-
Use DevOps when speed, automation, and ongoing improvements are important.
Learn to refrence Learn the vagrant