Introduction
In modern software development, setting up and managing consistent environments is often a big challenge. Developers face issues where an application works on one system but fails on another due to differences in configuration. Vagrant solves this problem by providing a lightweight, portable, and reproducible development environment.
What is Vagrant
Vagrant is an open-source tool used to create and manage portable virtual development environments. It’s mostly used by developers and DevOps engineers to ensure that everyone works in the same environment, avoiding the “it works on my machine” problem.
Virtual development Environment is an open-source software product for building and maintaining portable virtual software development environments; e.g., for VirtualBox, KVM, Hyper-V, Docker containers, VMware, and AWS. It tries to simplify the software configuration management of virtualization in order to increase development productivity
Simple Definition:
“Vagrant allows you to build and configure lightweight, reproducible, and portable development environments.”
How Vagrant Works:
-
You write a configuration file called
Vagrantfile. -
This file defines:
-
What operating system to use (Ubuntu, CentOS, etc.)
-
How much RAM/CPU to allocate
-
What software to install
-
-
Run the command
vagrant up-
Vagrant automatically downloads and sets up the virtual machine.
-
Key Features:
-
Works with VirtualBox, VMware, Docker, etc.
-
Quickly start or destroy virtual environments
-
Easy collaboration in teams using the same setup
Example :
This file sets up an Ubuntu virtual machine with 1GB RAM and maps port 8080 on your system to port 80 inside the VM
Why Use Vagrant?
Virtual development environment provides several advantages for developers and DevOps teams:
-
Consistency – Ensures the same environment across all developers.
-
Portability – The same environment can run on Windows, macOS, or Linux.
-
Automation – Automates environment setup using scripts.
-
Integration – Works with configuration management tools like Ansible, Puppet, and Chef.
-
Saves Time – No need to manually configure systems.
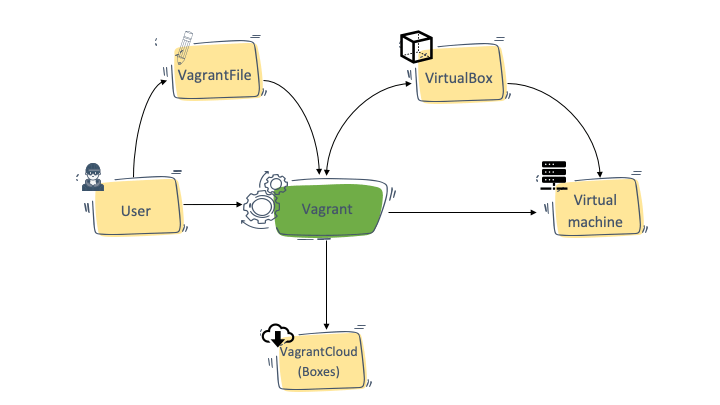
Vagrant Architecture
-
Virtual development environment file – A configuration file where you define the environment.
-
Provider – The virtualization backend (e.g., VirtualBox, VMware, Docker).
-
Provisioner – Tools that configure the environment (e.g., Ansible, Puppet).
Use Cases :
-
Software Development – Consistent environments for teams.
-
Testing – Easily test software in different OS configurations.
-
DevOps – Infrastructure as Code practice.
-
Education – Teaching environments for Linux, DevOps, and cloud computing.
Tools You Need:
-
VirtualBox (for virtualization)
-
Virtual development environment (main tool)
-
Optional: Ansible, Puppet, Chef (for automation)
Prerequisites:
-
Virtualization should be enabled in BIOS
-
Install VirtualBox
-
Install Virtual development environment from Install Now
Step-by-Step: How to Install Vagrant
For Windows:
Install VirtualBox (Required)
-
Visit: Click Here
-
Download and install the latest version of Oracle VirtualBox
-
Virtual development environment needs a provider to run virtual machines. VirtualBox is free and works well with Vagrant.
Download and Install Virtual development environment
-
Go to: https://www.virtual development environment up.com/downloads
-
Select Windows and download the installer.
-
Run the
.msiinstaller and follow the installation steps (Next > Next > Finish). -
Restart your system (if required).
Verify Installation
Open Command Prompt (CMD) or PowerShell and run:
You should see output like:
