WordPress Full Course-2025
What is WordPress?
WordPress is a free and open-source content management system (CMS) that allows you to create and manage websites easily, even if you don’t know how to code.

WordPress Definition

Two Versions of WordPress
| Version | Website | Description |
|---|---|---|
| WordPress.org | wordpress.org | Self-hosted, more control, free to use with custom hosting. |
| WordPress.com | wordpress.com | Hosted solution, easier to start, some features paid. |
What Can You Create with WordPress?
-
Blogs
-
Business websites
-
Online portfolios
-
E-commerce stores (with plugins like WooCommerce)
-
Membership sites
-
Educational websites
-
News & magazine portals
Why WordPress is Popular
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| 🔧 Easy to Use | No coding needed. Drag-and-drop block editor (Gutenberg). |
| 🎨 Themes | Choose from thousands of free and premium designs. |
| 🧩 Plugins | Extend functionality (SEO, contact forms, speed, security). |
| 🌍 SEO Friendly | Built-in SEO features + plugins like Rank Math or Yoast SEO. |
| 🌐 Multilingual Support | Create websites in different languages. |
| 🔐 Secure & Scalable | Regular updates, large community, and support. |
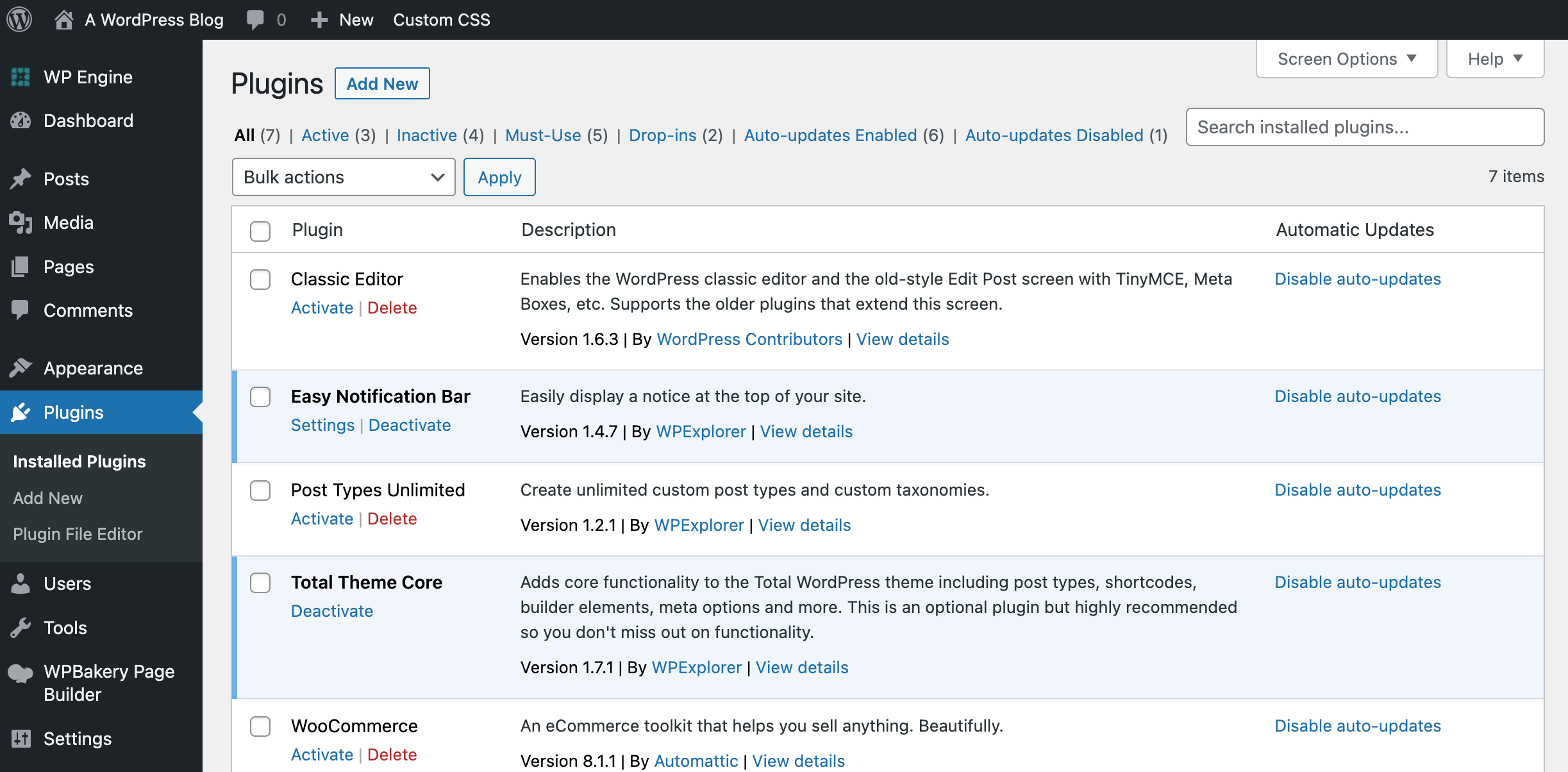
Basic WordPress Terms
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Post | Regular blog entries, listed by date. |
| Page | Static content like “About Us”, “Contact”. |
| Plugin | Add extra features (like forms, SEO, security). |
| Theme | Controls the look and layout of your website. |
| Dashboard | Admin area where you control your site. |
Example Use Case
You’re writing a blog titled “HTML 50+ Elements – Learn All Tags from Basic to Advanced” using WordPress.org with the Rank Math plugin for SEO and adding images, links, and formatted blocks using Gutenberg editor.
Subheading Ideas About WordPress
-
What is WordPress and Why is it So Popular?
-
Key Features of WordPress You Should Know
-
Types of Websites You Can Build with WordPress
-
Difference Between WordPress.com and WordPress.org
-
Advantages of Using WordPress for Your Website
-
Getting Started with WordPress: A Beginner’s Guide
-
Top Plugins to Supercharge Your WordPress Site
-
Choosing the Right Theme for Your WordPress Website
-
How to Create SEO-Friendly Content in WordPress
-
Understanding the WordPress Dashboard and Its Tools
-
WordPress vs Other CMS Platforms: A Quick Comparison
-
Common WordPress Errors and How to Fix Them
-
How to Customize Your Website with WordPress Blocks
-
Essential Security Tips for WordPress Users
-
How to Install WordPress on Localhost or Web Hosting
Response of all Subheading Ideas About WordPress
1. What is WordPress and Why is it So Popular?
WordPress is a free, open-source content management system (CMS) that allows users to build and manage websites without needing to code. It powers over 43% of websites globally because it’s flexible, user-friendly, and has a huge community for support.

2. Key Features of WordPress You Should Know
-
Easy-to-use dashboard
-
Thousands of free and premium themes
-
Powerful plugins for SEO, forms, eCommerce, etc.
-
Mobile-responsive design
-
Multilingual support
-
Gutenberg block editor for drag-and-drop content creation
3. Types of Websites You Can Build with WordPress
-
Personal blogs and portfolios
-
Business and corporate websites
-
Online stores (with WooCommerce)
-
News and magazine sites
-
Educational or membership portals
-
Event and booking sites
4. Difference Between WordPress.com and WordPress.org
| WordPress.com | WordPress.org |
|---|---|
| Hosted by WordPress | Self-hosted |
| Limited customization | Full control over site |
| Some features require payment | Most features are free |
| Good for beginners | Ideal for full-featured websites |
5. Advantages of Using WordPress for Your Website
-
No coding required
-
Cost-effective
-
SEO-friendly
-
Secure and scalable
-
Easy integration with tools like Google Analytics, email marketing, etc.
-
Huge support community and documentation
6. Getting Started with WordPress: A Beginner’s Guide
-
Choose a domain and hosting
-
Install WordPress (many hosts offer 1-click install)
-
Select a theme
-
Install necessary plugins (like SEO, security, backups)
-
Start creating posts and pages
-
Publish your website
7. Top Plugins to Supercharge Your WordPress Site
-
Rank Math – SEO optimization
-
Elementor – Page builder
-
WooCommerce – eCommerce store
-
WPForms – Drag-and-drop contact forms
-
Wordfence – Security
-
UpdraftPlus – Backup and restore
8. Choosing the Right Theme for Your WordPress Website
Pick a theme that is:
-
Mobile responsive
-
Lightweight and fast-loading
-
Customizable (supports page builders)
-
SEO-optimized
-
Regularly updated and well-reviewed
Popular themes: Astra, OceanWP, GeneratePress, Neve, Kadence
9. How to Create SEO-Friendly Content in WordPress
-
Use a focus keyword in title, URL, headings, and meta description
-
Optimize images (alt text, compression)
-
Use internal and external links
-
Structure content with headings (H1, H2, H3…)
-
Use SEO plugins like Rank Math or Yoast SEO
10. Understanding the WordPress Dashboard and Its Tools
The dashboard is the control panel for your site. From here you can:
-
Write posts and pages
-
Manage themes and plugins
-
Customize site appearance
-
Adjust settings
-
Monitor comments and users
-
Use tools like SEO, backups, etc.
11. WordPress vs Other CMS Platforms: A Quick Comparison
| CMS | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| WordPress | Easy, flexible, plugin-rich | Needs regular updates |
| Wix | Beginner-friendly | Less control |
| Shopify | Best for eCommerce | Paid only |
| Joomla | More powerful backend | Complex for beginners |
| Squarespace | Beautiful designs | Limited customization |
12. Common WordPress Errors and How to Fix Them
-
Error establishing a database connection → Check
wp-config.phpcredentials -
White screen of death → Disable plugins or theme via FTP
-
404 page not found → Re-save permalink settings
-
Locked out of admin → Reset password via email or phpMyAdmin
13. How to Customize Your Website with WordPress Blocks
WordPress’s Gutenberg editor allows you to add content as blocks:
-
Paragraph, heading, image, gallery, video, button, list, quote, etc.
-
You can rearrange, group, duplicate, and style blocks easily
-
Add custom blocks using plugins or page builders like Elementor
14. Essential Security Tips for WordPress Users
-
Use strong passwords and 2FA
-
Install security plugins (Wordfence, Sucuri)
-
Keep WordPress, plugins, and themes updated
-
Use SSL certificate (HTTPS)
-
Limit login attempts
-
Backup your site regularly
15. How to Install WordPress on Localhost or Web Hosting
On Web Hosting:
-
Choose a host (e.g., Bluehost, Hostinger)
-
Use 1-click WordPress install from hosting panel
-
Set up your admin username and password
On Localhost (PC):
-
Install XAMPP/WAMP
-
Download WordPress from wordpress.org
-
Create a database via phpMyAdmin
-
Extract WordPress folder into
htdocs -
Run
localhost/wordpressin your browser to install
How WordPress Works – Step-by-Step Explanation
WordPress works as a Content Management System (CMS) that helps you create, manage, and publish websites or blogs without needing advanced technical skills.

Here’s a simple breakdown of how WordPress works:
1. Installation
-
You install WordPress on a web server (like Bluehost, Hostinger, or locally via XAMPP).
-
It creates essential files and a database to store your content (like posts, users, settings, etc.).
2. Admin Dashboard (Backend)
-
After login (via
yourdomain.com/wp-admin), you access the dashboard. -
This is your control panel to:
-
Write posts and pages
-
Install themes and plugins
-
Manage users
-
Configure settings (SEO, security, etc.)
-
3. Themes Control Design (Appearance)
-
A WordPress theme controls the look and layout of your site.
-
You can install free or premium themes and customize them without coding.
4. Plugins Add Functionality
-
Plugins are tools you can install to add features like:
-
Contact forms
-
SEO tools
-
E-commerce (WooCommerce)
-
Backup and security
-
-
Example: Install “Rank Math” to improve SEO easily.
5. Gutenberg Editor – Block-Based Content
-
WordPress uses a block editor (Gutenberg) to create content:
-
Add blocks for text, images, videos, buttons, lists, etc.
-
Drag-and-drop layout for easy formatting.
-
6. Database and PHP – Behind the Scenes
-
WordPress uses PHP to fetch data from a MySQL database.
-
For example:
-
You create a post → WordPress stores it in the database.
-
A user visits your site → PHP retrieves and displays the content on the theme.
-
7. Visitors See the Frontend
-
When someone visits your website (e.g.,
yourblog.com):-
WordPress loads the requested page/post.
-
Combines the content + theme + plugins to show the final webpage.
-
All this happens dynamically and instantly.
-
8. SEO & Performance Optimization
-
Use plugins (like Rank Math, W3 Total Cache, etc.) to:
-
Improve load speed
-
Optimize images
-
Set meta titles/descriptions
-
Make the site mobile-friendly
-
FlowChat of WordPress Works – Step-by-Step Explanation
You (Admin)
⬇️
Dashboard (Write, Customize, Manage)
⬇️
WordPress Core + Themes + Plugins
⬇️
Database (Stores Content)
⬇️
Visitor Requests Page
⬇️
WordPress Delivers Page to Visitor’s BrowserTypes of WordPress
There are two main types of WordPress platforms:
1. WordPress.com (Hosted Platform)
Website: www.wordpress.com
What it is:
-
A hosted service where everything (hosting, security, updates) is managed for you.
-
Great for beginners who want a simple blog or small site.
Features:
-
No need to buy separate hosting
-
Easy to set up
-
Free plan available (with limited features)
-
Paid plans offer more control, themes, and plugins
Limitations:
-
Limited customization unless you upgrade to a paid plan
-
Can’t upload custom plugins on free plan
-
You don’t have full control of your files or database
2. WordPress.org (Self-Hosted WordPress)
Website: www.wordpress.org
What it is:
-
The free, open-source WordPress software you can download and install on your own web hosting.
-
Gives you full control over your website.
Features:
-
100% customizable (themes, plugins, code)
-
Install any plugin or theme
-
Great for blogs, business sites, eCommerce (with WooCommerce)
-
You own your site and data
Requirements:
-
You must purchase hosting and domain
-
You are responsible for updates, backups, and security (can be automated with plugins)
WordPress Blog & Content Goals
-
You are writing a blog post about HTML elements titled “HTML 50+ Elements – Learn All Tags from Basic to Advanced.”
-
Your focus is on creating educational, SEO-friendly content from basic to advanced HTML.
-
You want to optimize the post for SEO, and you are using the Rank Math plugin for guidance.
Common WordPress Tasks & Issues You’ve Asked About
-
SEO Optimization with Rank Math:
-
Errors like:
-
“Focus Keyword not in URL”
-
“Focus Keyword not in Meta Description”
-
“Keyword Density is low”
-
“Add image with Focus Keyword as alt text”
-
“Title doesn’t contain a power word or number”
-
-
Goal: Fix these errors to turn all Rank Math indicators green.
-
-
Content Writing:
-
Writing and formatting content for all HTML tags.
-
Adding examples for each tag like
<a>,<img>,<ul>,<div>, etc. -
Using screenshots and diagrams to explain content visually.
-
-
Image Issues:
-
Creating and improving diagrams and images for HTML structures.
-
Adding alt text with keywords for SEO.
-
Fixing errors where image keywords were not recognized by Rank Math.
-
-
Block Editor (Gutenberg):
-
You asked: “Apne linkin main block kaise dale WordPress se” – meaning you want to know how to insert links using blocks in WordPress.
-
Suggestions Given So Far
-
Include focus keyword in:
-
URL
-
SEO title
-
Meta description
-
Image alt text
-
First 10% of the content
-
-
Use power words and numbers in your title (e.g., “50+ HTML Tags You Must Know”).
-
Maintain keyword density between 1–2%.
-
Use images with relevant filenames and optimize them before uploading.
-
Use headings (H2, H3) properly for better structure and SEO.
What is Elementor?
Elementor is a drag-and-drop page builder plugin for WordPress that helps you create beautiful, responsive pages without writing any code.
Steps to Create a Page with Elementor
1. Install and Activate Elementor
-
Go to your WordPress Dashboard.
-
Navigate to Plugins > Add New.
-
Search for “Elementor Website Builder“.
-
Click Install Now → Then click Activate.
-
Optionally, you can install Elementor Pro for more widgets and templates.
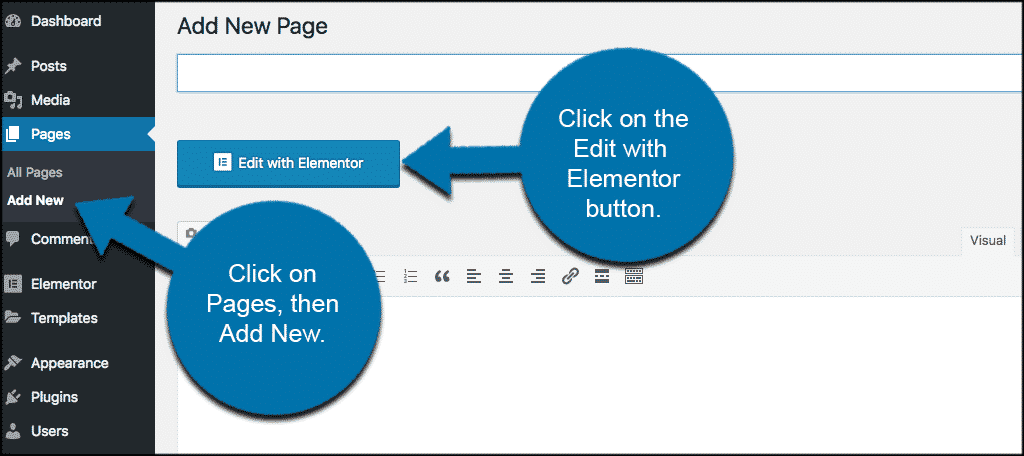
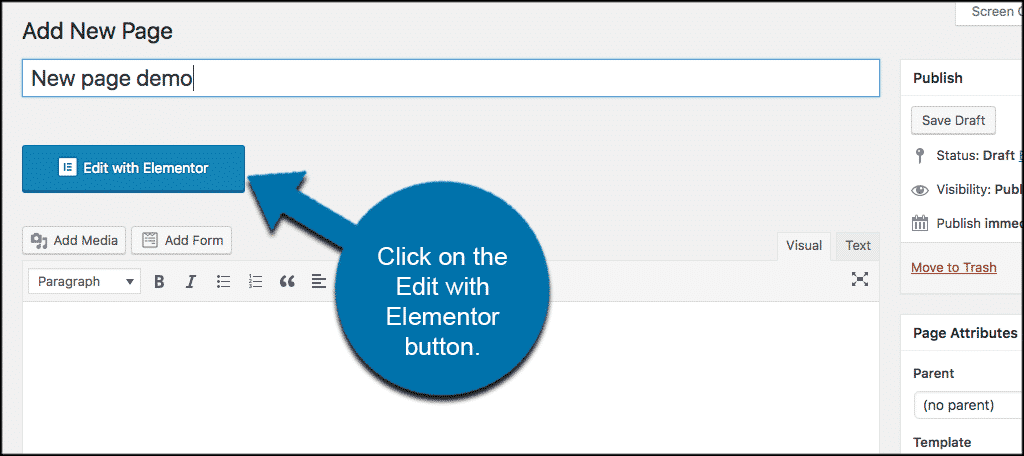
2. Create a New Page
-
Go to Pages > Add New.
-
Give your page a title (e.g., “Home”, “About Us”).
-
Click the “Edit with Elementor” button.
3. Using Elementor Interface
Once Elementor loads, you’ll see two main sections:
-
Left Panel: Contains widgets (Text, Image, Button, Heading, Video, etc.)
-
Right Side: Live preview of your page
4. Add Elements to the Page
-
Click the “+” button to add a new section.
-
Choose your layout structure (1 column, 2 columns, etc.).
-
Drag widgets from the left panel into your section (like “Heading”, “Text Editor”, or “Image”).
-
Customize each element using the Style and Advanced tabs.
5. Customize the Design
-
Change fonts, colors, margins, paddings, backgrounds.
-
Use buttons, icons, image galleries, and animations.
-
Add YouTube videos, maps, and forms.
6. Use Pre-Built Templates (Optional)
-
Click the Folder 📁 icon next to the “+” to open the Elementor Template Library.
-
Choose a free or pro template and click Insert.
-
Edit the template as you like.
7. Preview and Publish
-
Click the eye icon 👁️ to preview your page.
-
When you’re happy, click “Publish”.
Why Choose WordPress Full Course 2025?
-
The WordPress Full Course 2025 offers a step-by-step learning path from beginner to expert level.
-
Whether you’re a student or a business owner, the WordPress Full Course 2025 will help you build stunning websites without coding.
-
Our WordPress Full Course 2025 is designed with the latest tools like Elementor, SEO plugins, and advanced themes.
Learn WordPress full course by video
learn html full course click here


